Back pain is a common issue affecting millions of people worldwide, impacting their daily lives and overall well-being. Whether it’s a dull ache or sharp, stabbing pain, back ache can be debilitating, leading to missed workdays and decreased quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for back pain is crucial for managing and preventing it. In this blog, we’ll explore everything you need to know about spinal discomfort.
Understanding Back Pain
Back pain can range from a mild, nagging discomfort to severe, chronic pain that limits mobility and function. It is usually classified into three main types:
- Lower Back Pain: The most common type, often caused by muscle strain, poor posture, or disc problems.
- Middle Back Pain: Less common and usually related to underlying health conditions like osteoporosis.
- Upper Back Pain: Often caused by muscle strain or injuries, but can also be linked to issues like scoliosis.
Delve into our comprehensive blog on Lower vs. Upper Back Pain for a profound understanding.
Common Causes of Back Pain
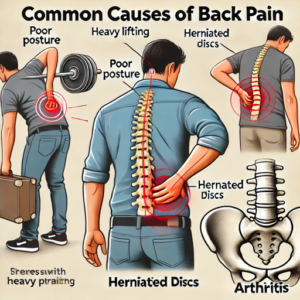
Back ache can result from various factors, ranging from lifestyle habits to medical conditions. Some of the most common causes include:
- Muscle Strain and Sprains: Overexertion, lifting heavy objects incorrectly, or sudden movements can cause muscle strain, leading to back pain.
- Poor Posture: Sitting or standing improperly for extended periods puts stress on the back, leading to discomfort and pain. Learn more about the impact of poor posture on back health.
- Herniated Discs: When the soft tissue inside the discs between vertebrae protrudes, it can press on nerves, causing pain.
- Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis can cause inflammation in the joints, leading to chronic back ache.
- Osteoporosis: Weak and brittle bones can cause fractures in the spine, leading to severe ache.
- Scoliosis: A curvature of the spine that can lead to pain if the condition worsens over time.
- Smoking: Smoking reduces blood flow to the spine, accelerating disc degeneration and increasing the risk of back pain. Discover more about how smoking contributes to back pain.
- Body Weight: Excess body weight puts additional stress on the spine and back muscles, making back pain more likely. Read about the relationship between weight and back pain.
Symptoms of Back Pain
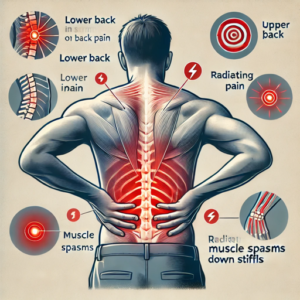
The symptoms of back pain can vary depending on the cause and severity. Common symptoms include:
- Localized Pain: Pain confined to a specific area of the back.
- Radiating Pain: Pain that spreads from the back to other parts of the body, such as the legs or arms.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the back, especially after periods of inactivity.
- Muscle Spasms: Sudden, involuntary contractions of the muscles that can cause sharp ache.
- Numbness or Tingling: Sensory symptoms that may accompany nerve-related back pain.
If you’re experiencing pain around your ribs and back, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment. They can help determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate interventions.
Diagnosis of Back Pain
Diagnosing the cause of back pain is essential for effective treatment. Healthcare providers typically use the following methods:
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the back, along with a discussion of symptoms and medical history.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans are used to visualize the spine and identify issues like herniated discs or fractures.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests, such as the Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR), C-Reactive Protein (CRP), and Complete Blood Count (CBC), can help identify underlying conditions like inflammation or infections that may be contributing to spinal discomfort.
Treatment Options for Back Pain

Treatment for back ache varies depending on the cause and severity. Common treatment options include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen and acetaminophen are commonly used for back ache. Muscle relaxants such as cyclobenzaprine or anti-inflammatory drugs like naproxen may also be prescribed.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches designed to strengthen the back muscles and improve flexibility. Learn how physiotherapy exercises can help you move freely again.
- Chiropractic Care: Spinal adjustments and manipulations to alleviate pain and improve function.
- Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can help relax tense muscles and relieve pain.
- Acupuncture: An alternative treatment that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to relieve pain. Explore the benefits of acupressure points for back pain relief.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or ice to the affected area can reduce inflammation and provide pain relief. Discover the benefits of heat and ice therapy for back pain.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to address issues like herniated discs or spinal fractures.
- Yoga: Practicing yoga can help improve flexibility, strengthen the core muscles, and reduce stress, all of which can alleviate spinal discomfort. Specific yoga poses are designed to stretch and strengthen the back, promoting better spinal health. Learn more about yoga for back pain relief.
- Diet and Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can support overall spine health. Foods like leafy greens, fish high in omega-3 fatty acids, nuts, and seeds can reduce inflammation and contribute to a healthy weight, both of which are crucial for managing back pain. Explore the best diet for back pain relief.
- Pain Relief Devices: Devices such as TENS units (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) and heat pads can provide non-invasive pain relief by stimulating nerves or applying heat to the affected area.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Incorporating practices like meditation, mindfulness, and deep breathing exercises can help manage the perception of pain by reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
- Alternative Treatments: Other alternative treatments like acupuncture, chiropractic care, and herbal supplements can also provide relief. Learn about alternative treatments for back pain.
Preventing Back Pain
Preventing back ache is often easier than treating it. Here are some tips to keep your back healthy:
- Posture Improvement: Maintain good posture when sitting, standing, and lifting heavy objects. Use ergonomic furniture and equipment when possible.
- Exercise and Strengthening: Regular exercise, especially core strengthening exercises, can help support the spine and prevent spinal discomfort.
- Ergonomics: Adjust your workspace to reduce strain on your back. Ensure your chair, desk, and computer are at the correct height. To understand more about it, read our blog on ergonomic workspace setup to prevent back pain
- Healthy Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on your back muscles and spine.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: Bend at the knees, not at the waist, when lifting heavy objects, and keep the load close to your body.
- Supportive Footwear: Wearing shoes that provide proper arch support can help reduce strain on your back. Avoid high heels and opt for shoes that offer good cushioning and alignment for your feet. For better understanding read our blog on best shoes for back pain
- Adjusting Sleep Position: Your sleep position can significantly affect your back pain. Sleeping on your back with a pillow under your knees or on your side with a pillow between your knees can help maintain the natural curve of your spine and reduce pain. For more detail read our blog on best sleep position for back pain relief
- Regular Check-ups: Regular visits to your healthcare provider can help catch potential issues early and prevent back ache from developing.
Living with Chronic Back Ache
For those living with chronic back pain, managing the condition involves a combination of treatments and lifestyle adjustments:
- Pain Management Strategies: Developing a pain management plan with your healthcare provider, including medications, physical therapy, and alternative treatments.
- Mental Health and Back Pain: Chronic pain can take a toll on mental health. It’s essential to seek support from mental health professionals if needed.
- Support Systems: Rely on friends, family, and support groups to help you cope with chronic pain.
- Long-term Care and Maintenance: Ongoing care, including regular exercise, proper posture, and lifestyle adjustments, can help manage chronic back ache.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Incorporating practices like meditation, mindfulness, and deep breathing exercises can help manage the perception of ache by reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
When to See a Doctor
While most spinal discomfort can be managed with self-care, certain symptoms require immediate medical attention:
- Red Flags: Severe pain that doesn’t improve with rest, pain that radiates down the legs, numbness or tingling, loss of bladder or bowel control, or unexplained weight loss.
- Self-Care vs. Professional Care: Knowing when to seek help can prevent minor issues from becoming serious.
Future of Back Pain Management
The future of back pain management looks promising, with emerging treatments and ongoing research providing new hope for those suffering from this condition:
- Emerging Treatments: Innovations in medical technology, such as regenerative medicine, offer new possibilities for back ache relief.
- Research and Development: Ongoing studies continue to explore the causes of spinal discomfort and develop more effective treatments.
- Integrative Medicine: Combining traditional and alternative therapies for a holistic approach to back ache management.
Conclusion
Back pain is a prevalent issue that can significantly impact your quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help you manage and prevent Spinal discomfort effectively. If you experience severe or, chronic muscle and spine pain , don’t hesitate to seek professional medical advice. By taking proactive steps to care for your back, you can lead a healthier, ache-free life.
